Creating effective learning objectives with AI (or without!) is the foundation of any successful instructional design and e-learning initiative. They guide learners and provide a roadmap for achieving desired outcomes.
Just imagine a world where crafting the perfect learning objectives for your courses and programs is not just a time-consuming task but a breeze, where these objectives are not just ordinary but extraordinary in guiding learners towards their goals.
In this blog post, we will explore how an AI assistant can revolutionize the process of creating the best learning objectives. We’ll unveil the ways in which AI can not only streamline the process but also enhance the quality of your learning objectives, ultimately leading to improved learning outcomes.
By leveraging the power of AI technology, instructional designers, teachers, and learners can enhance the effectiveness and relevance of their learning objectives, resulting in improved learning outcomes.
Learn more about Exploring the Future: Instructional Design and AI.
In this post
- TL;DR
- How AI Can Help Write Learning Objectives
- ABCD vs. SMART: Frameworks for Learning Objectives
- Step 1: Identify the Desired Learning Outcomes
- Utilizing SMART Criteria
- Useful Desired Learning Outcomes Prompts
- Step 2: Choose the Appropriate Level of Learning
- Leveraging Bloom’s Taxonomy
- Useful Level of Learning Prompts
- Step 3: Write the Learning Objectives
- Crafting Clear and Concise Objectives
- Useful Writing Learning Objectives Prompts
- Step 4: Double-check your Learning Objectives with AI
- FAQ
- Useful Links: Effective Learning Objectives with AI
- Conclusion
TL;DR
In this blog post about creating effective Learning Objectives with AI, we explore how AI can enhance the process of creating effective learning objectives. AI offers assistance in various ways, from improving language in objectives to aligning them with learning outcomes and providing personalization. We also delve into the ABCD and SMART frameworks for learning objectives.
The step-by-step guide covers identifying desired outcomes, choosing the right level of learning with Bloom’s Taxonomy, and writing clear objectives. AI can assist at every stage, but human understanding remains crucial. Finally, we emphasize that AI enhances, not replaces, instructional design.
How can AI help me Write Learning Objectives?
AI can assist you in writing learning objectives in several ways:
- Language Assistance: AI-powered tools can analyze your learning objectives and provide suggestions for improved wording and structure. These tools can identify errors, offer alternative phrasing, and help make objectives more concise and clear.
- Alignment with Learning Outcomes: AI can analyze learning objectives against desired learning outcomes and provide feedback on alignment. By comparing the objectives to a defined set of outcomes, AI assistants can ensure that your objectives are well-aligned and support the overall goals of the course or program.
- Personalization: AI assistants can help you customize learning objectives based on individual learner needs. By analyzing learner data and preferences, AI can suggest personalized learning objectives that cater to specific learning styles, levels of proficiency, or career goals. This personalization enhances learner engagement and motivation.
- Feedback and Suggestions: AI assistants can provide valuable feedback on the quality, clarity, and alignment of your learning objectives. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, AI assistants can identify patterns and best practices, offering insights and suggestions to enhance the effectiveness of your objectives.
- Efficiency and Time-saving: AI can automate the process of writing and reviewing learning objectives, saving you time and effort. AI assistants can quickly analyze large amounts of data, generate objective templates, and provide instant feedback, allowing you to focus on other important aspects of your instructional design process.
By harnessing AI technology, you can leverage its capabilities to streamline the process of crafting and improving learning objectives. AI assistants provide valuable support by offering language assistance, alignment with learning outcomes, personalization, adaptive learning, feedback, and time-saving efficiency.
Creating Effective Learning Objectives with AI as a tool will enhance the quality and impact of your instructional design efforts.

Creating Effective Learning Objectives with AI: A Step-by-Step Guide
When you are creating effective Learning Objectives with AI (or without), you should be clear about ABCD and SMART.
What is the difference between ABCD and SMART?
ABCD and SMART are two frameworks for creating effective learning objectives.
- ABCD stands for Audience, Behavior, Condition, and Degree: By the end of this lesson, students (audience) will be able to write (behaviour) a short summary of a text (condition) with no more than two errors (degree).
- SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound: By the end of this course, students will be able to write (specific and measurable) a five-page research paper (achievable and relevant) within two weeks (time-bound).
Both frameworks help to define clear and observable outcomes for learners. However, they have some differences. ABCD focuses more on the behaviour and performance of the learners, while SMART focuses more on the characteristics and quality of the objective. ABCD is often used for lesson-level objectives, while SMART is often used for course-level or program-level objectives.
Step 1: Identify the Desired Learning Outcomes
To create impactful learning objectives, start by clearly defining the desired learning outcomes. What should the learner be able to do at the end of your course?
Utilize the SMART criteria to ensure your objectives are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. SMART objectives provide a framework for setting clear and realistic goals that align with the overall course objectives.
Useful Desired Learning Outcomes Prompts
The following prompts can assist you in defining the desired learning outcomes with the help of AI.
🤖
- Write a SMART learning outcome for a [level]-level [type] on [topic].
- Write a SMART learning outcome for a [level]-level [type] on [topic]. The learning objective should start with “[verb]” and end with “[criteria]”.
Here are three example prompts for step 1 to achieve the best outcomes:
- Write a SMART learning outcome for a beginner-level course on web development.
- Write a SMART learning outcome for an intermediate-level project on writing a blog post. The learning outcome should start with “After completing this course, you will be able to”.
- Write a SMART learning outcome for an advanced-level lesson on solving a math problem. The learning objective should start with “By the end of this lesson, you will be able to” and end with “creating graphs, tables, and diagrams”.
🤖
Step 2: Choose the Appropriate Level of Learning
Bloom’s taxonomy serves as a valuable tool for determining the level of cognitive skills and knowledge required for successful learning. By categorizing learning objectives into various levels, such as remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating, you can ensure a comprehensive and progressive learning experience for your learners.
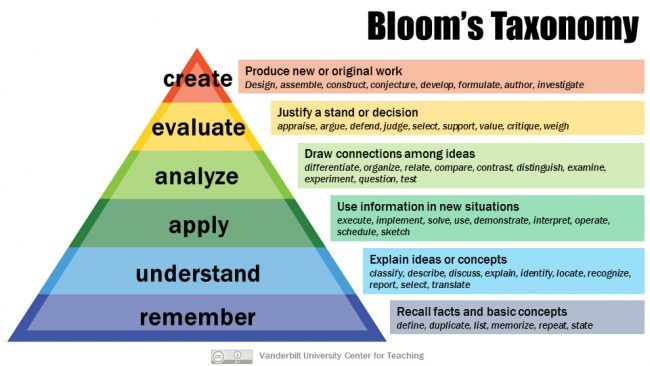
Sometimes it is difficult to identify the ideal levels of learning, especially in fields you are not an expert in. AI can identify appropriate levels of learning better than humans because it can process large amounts of data. It identifies patterns that humans cannot see, so why not use this power in your work as an instructional designer or educator?
Useful Level of Learning Prompts
🤖 Here are ten example prompts on how AI can assist in choosing the appropriate level of learning through Bloom’s taxonomy:
- Generate a list of [number] of learning objectives for a course on [topic] using Bloom’s taxonomy. Each learning objective should start with a verb that corresponds to one of the six levels of the cognitive domain: remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, or create.
- Analyze the following learning objective for a lesson on [topic]: “[learning objective]”. Identify which level of Bloom’s taxonomy it belongs to and explain why.
- Evaluate the following learning objective for a project on [topic]: “[learning objective]”. Use the SMART criteria to determine if it is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Create a quiz question for a unit on [topic] that tests the students’ ability to [verb] the [concept]. Provide four multiple-choice options and indicate the correct answer.
- Apply Bloom’s taxonomy to design a rubric for assessing a student’s performance on a [type] about [topic]. Include criteria and descriptors for each level of cognitive domain.
- Remember the main features and benefits of Bloom’s taxonomy and summarize them in your own words.
- Understand the difference between the original and revised versions of Bloom’s taxonomy and compare them using a Venn diagram.
- Analyze the following learning objective for a course on [topic]: “[learning objective]”. Identify the knowledge, skills, and attitudes that are involved in achieving this objective.
- Evaluate the following learning objective for a lesson on [topic]: “[learning objective]”. Use Bloom’s taxonomy to suggest ways to improve it or make it more challenging.
- Create a learning objective for a project on [topic] that requires the students to use the highest level of Bloom’s taxonomy. Explain how you would measure or assess the students’ achievement of this objective.
Examples with Bloom’s Taxonomy
- Generate a list of learning objectives for a course on digital photography using Bloom’s taxonomy. Each learning objective should start with a verb that corresponds to one of the six levels of the cognitive domain: remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, or create.
- Analyze the following learning objective for a lesson on fractions: “Students will be able to compare and order fractions with different denominators.” Identify which level of Bloom’s taxonomy it belongs to and explain why.
- Evaluate the following learning objective for a project on climate change: “Students will be able to design and implement a plan to reduce their carbon footprint.” Use the SMART criteria to determine if it is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Create a quiz question for a unit on the American Revolution that tests the student’s ability to evaluate the causes and effects of the war. Provide four multiple-choice options and indicate the correct answer.
- Apply Bloom’s taxonomy to design a rubric for assessing a student’s performance on a presentation about their favourite book. Include criteria and descriptors for each level of cognitive domain.
- Analyze the following learning objective for a course on web development: “Students will be able to create a simple website using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.” Identify the knowledge, skills, and attitudes that are involved in achieving this objective.
- Evaluate the following learning objective for a lesson on poetry: “Students will be able to write a poem using a rhyme scheme of ABAB.” Use Bloom’s taxonomy to suggest ways to improve it or make it more challenging.
Step 3: Write the Learning Objectives
Crafting concise and effective learning objectives is crucial for guiding learners and keeping them engaged. But that can be a very time-consuming process, especially if you are not a subject matter expert. AI can help in defining optimal learning objectives.
Use action verbs to communicate what learners will be able to do after completing the course or module. Measurable indicators, such as the ability to solve specific problems or demonstrate mastery of a concept, should accompany each objective. Tips for writing clear and concise objectives include using simple language, avoiding jargon, and focusing on specific skills or knowledge.
Useful Writing Learning Objectives Prompts
Finally, similar to prompting for learning outcomes, we can use the same tech to ask for learning objectives.
🤖
- Write a SMART learning objective for a [level]-level [type] on [topic].
- Write a SMART learning objective for a [level]-level [type] on [topic]. The learning objective should start with “[verb]” and end with “[criteria]”.
Here are three example prompts for step 3 to achieve the best outcomes:
- Write a SMART learning objective for a beginner-level course on web development.
- Write a SMART learning objective for an intermediate-level project on writing a blog post. The learning objective should start with “After completing this course, you will be able to”.
- Write a SMART learning objective for an advanced-level lesson on solving a math problem. The learning objective should start with “By the end of this lesson, you will be able to” and end with “creating graphs, tables, and diagrams”.
From my experience, all AI can create valuable insights for the learning objectives of your course. Often, you will not even have to make significant adjustments. But human oversight and holistic understanding should never be underestimated.
Instructional Designers and Educators will often grasp the complexity and special requirements of specific target groups or individuals better than AI.
However, once you forge the learning objectives to your liking, follow the last and final step.
Learn more about my AI experiments! Which AI is Best for Generating Learning Objectives?
Step 4: Double-check your Learning Objectives with AI
Testing your learning objectives to ensure they are measurable and achievable can be perfectly done with AI.
Useful Learning Objectives Prompts
Here’s how instructional designers can use AI to double-check learning objectives:
- Evaluate the following learning objectives. Use the SMART criteria to determine if it is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
[INSERT LEARNING OBJECTIVES] - Analyze the following learning objectives. Identify which level of Bloom’s taxonomy it belongs to and explain why.
[INSERT LEARNING OBJECTIVES]
FAQ: on AI-Powered Learning Objectives
Click here to open the FAQ
Q1: How can AI assist in writing learning objectives?
AI offers valuable assistance in crafting learning objectives. It can analyze your objectives, suggest improvements, align them with learning outcomes, provide personalization, enable adaptive learning, offer feedback, and save time through automation.
Q2: What are ABCD and SMART frameworks for learning objectives?
- ABCD focuses on Audience, Behavior, Condition, and Degree. For example, “By the end of this lesson, students (audience) will be able to write (behaviour) a short summary of a text (condition) with no more than two errors (degree).”
- SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. For instance, “By the end of this course, students will be able to write (specific and measurable) a five-page research paper (achievable and relevant) within two weeks (time-bound).”
Q3: How can I identify the desired learning outcomes?
To identify desired learning outcomes, start by clearly defining what learners should achieve by the end of your course. Utilize the SMART criteria to ensure your objectives are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Q4: What is Bloom’s Taxonomy, and how can AI help in choosing the right level of learning?
Bloom’s Taxonomy categorizes learning objectives into levels such as remembering, understanding, applying, and more. AI can assist by processing data and identifying appropriate levels, especially in areas where expertise might be lacking.
Q5: How can I craft clear and concise learning objectives?
Crafting clear objectives involves using action verbs to communicate what learners will achieve, focusing on measurable indicators, keeping the language simple, avoiding jargon, and emphasizing specific skills or knowledge.
Q6: Why is it essential to double-check learning objectives with AI?
Double-checking with AI ensures that your objectives are measurable and achievable, enhancing their quality and impact on learning outcomes.
Q7: Does AI replace instructional designers in creating learning objectives?
No, AI doesn’t replace instructional designers; it enhances their work. AI makes the process more efficient, accurate, and personalized, allowing instructional designers to focus on the nuances of individual learner needs.
Conclusion: Use an AI Assistant to Optimize Learning Objectives
Creating the best learning objectives is critical to instructional design and e-learning. By incorporating AI assistants into the process, instructional designers, teachers, and learners can enhance the quality and alignment of their learning objectives.
You can optimise your learning objectives for maximum impact through the steps mentioned above, including identifying desired outcomes, selecting appropriate cognitive levels, writing concise objectives, and utilizing AI assistants.
Remember, the goal of crafting effective Learning Objectives with AI in this context is not to replace instructional designers but to provide them with powerful tools to enhance their work. AI offers a way to make designing and checking learning objectives more efficient, accurate, and personalized.
Embrace the power of AI to create engaging and effective learning experiences that will elevate your instructional design efforts to new heights.
Valuable Links: Effective Learning Objectives with AI
- Artificial Intelligence in Education: This article by UNESCO discusses the potential of AI in addressing some of the biggest challenges in education today and how it can innovate teaching and learning practices.
- Using AI Tools to Lesson Plan: This article on Edutopia provides practical examples of how AI tools like ChatGPT can help educators find activities set up to teach designated skills.
- Learning Objectives Builder: Arizona State University’s Teach Online provides a Learning Objectives Builder tool that can help create effective learning objectives.
- AI SMART Goal Generator: Taskade offers an AI SMART Goal Generator that can be used to generate SMART goals and achieve success. (This is an affiliate link)
- AI Tools in Teaching and Learning: This article from Stanford University’s Teaching Commons discusses the effectiveness of assignments that support students in developing linked thinking and writing skills when teaching with AI tools.
Join the Conversation!
We value your perspective. Have you had firsthand experience in creating effective Learning Objectives with AI? We’d love to hear from you.
Share Your Insights: Leave a comment below and tell us about your encounters with AI-powered learning objectives. How has it impacted your teaching or learning experience?
Your voice matters, and together, we can explore the exciting possibilities AI brings to the world of education.