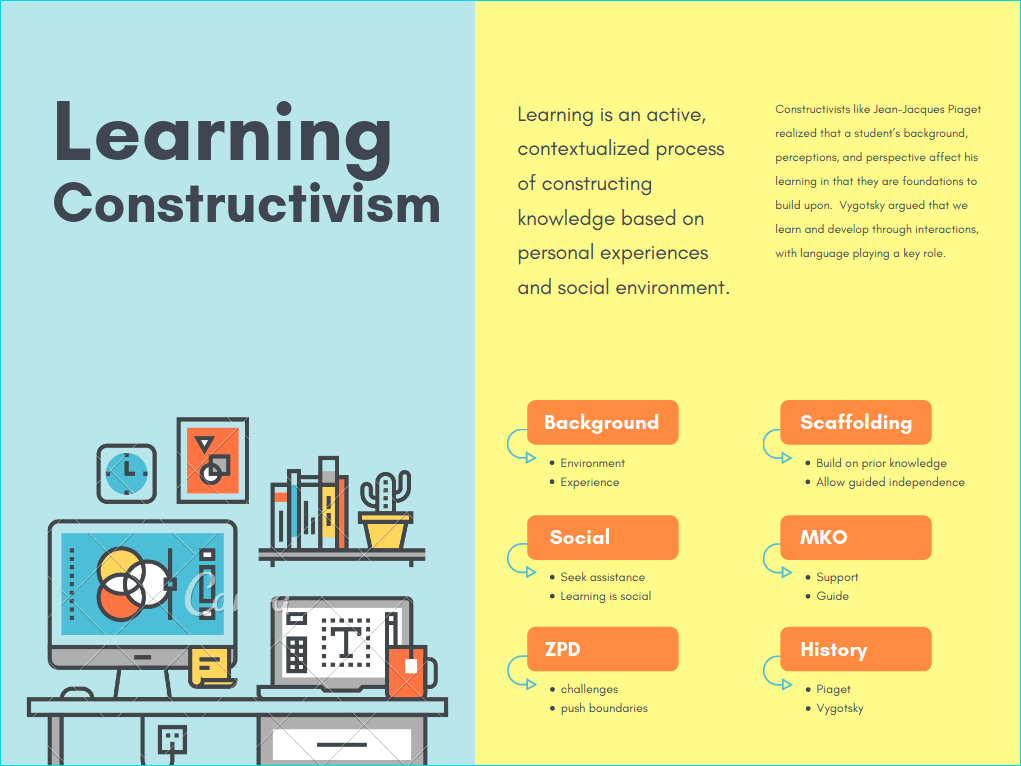
Constructivism is a learning theory that asserts that each student constructs his own learning and knowledge.
Constructivism recognizes the importance of students’ active engagement in the learning process; thus, learning objectives written for a constructivist setting are student-centered.
A student’s background, perceptions, and perspective affect his learning in that they are foundations to build upon.
Constructivism Infographic
Constructivist Approach in Customer Service
In order to compare the behaviorist approach with constructivsm, I will use the learning scenario created and posted in the USMx: LDT100x Instructional Design and Technology: Learning Theories forums as well as in the Behaviorism Learning Theory page
I will apply the theory of constructivism to create additional learning that complements and adds to the initial behaviorist scenario. (Posted here on edx)
Additional Learning through Constructivism
Since the learning environment, a call center, is per default a very social environment, constructivist elements can be added naturally. The focus lies on an active role of the agents to learn and develop new knowledge through collaboration.
- MKO-Principle: Vygotsky’s principle of social learning and the More Knowledgeble Other leads to several practices that can improve learning
- Younger call center agent can watch experienced analysts do their job and learn best practices
- Experienced analysts can watch the newer agents do their job and provide help and advice
- Creating groups of analysts with mixed experiences; these groups have to solve tasks together and can share best practices and knowledge
- Create knowledge actively: Since a lot of applications were complex, but the standard procedures are always the same, you can create scenarios where newer agents apply their current knowledge to learn a new application by constructed exercise. Given this scenario, they actively expand their skills within their ZPD (Zone of proximal development) Applying the methods (treating customers, finding processes in knowledge base etc.) they can explore new apps through a guided exercise approach.
- Learning to Learn: The above exercise not only serves the agents to learn new applications, but teaches them how to approach new issues and problems they might have never faced before. Since customer questions can be out of the box and outside of standard and typical procedures, training agents on improvising based on their current skills and finding knowledge and solutions can be very beneficial.
- Collaboration: Practice typical real world scenarios with the other learners. Customer Service is contact with clients. In order to train agents, you can create scenarios where they practice with each other. One takes the role of the agent, the other one takes the role of the customer. This social interaction benefits not only their skill as agent, but improves team spirit and broadens their perspective on their work, by getting into the shoes of the customer as well.
Zone of Proximal Development
As discussed above, the theory of proximal development will lead to the following skills
- Find relevant knowledge independently
- Identify MKOs and practice how to solve problems with their help
- Learn new applications by applying known processes and skills
- Gain the ability to improvise (when knowledge has not been trained before)
- Improved stress resistance since agents practice scenarios where they do not dominate the process, which might cause stress in direct customer contact
Scaffolding Strategy
Instructional scaffolding is the support given to a student by an instructor throughout the learning process. This support is specifically tailored to each student; this instructional approach allows students to experience student-centered learning, which tends to facilitate more efficient learning than teacher-centered learning
Bruner’s theory of scaffolding emerged around 1976 as a part of social constructivist theory, and was particularly influenced by the work of Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky
Bruner believed that when children start to learn new concepts, they need help from teachers and other adults in the form of active support. To begin with, they are dependent on their adult support, but as they become more independent in their thinking and acquire new skills and knowledge, the support can be gradually faded.
In a very specific way, scaffolding represents a reduction in the many choices a child might face, so that they become focused only on acquiring the skill or knowledge that is required.
Social Constructivist Strategy
- Reality is constructed through human activity
- Members of a society together invent the properties of the world.
- People create meaning through their interactions with each other and the objects in their environment.
- Learning is a social process.
- It occurs when people are engaged in social activities.
HERBERT ,
Sir thank you for posting your work. Since, It can help students like me to be refresh with this information. This can help us to have a reading review to help us recall what we already learn. Take Care Sir.